E Ample Of A Repeated Measures Design
E Ample Of A Repeated Measures Design - Web in this post, i’ll highlight the advantages and disadvantages of using a repeated measures design and show an example of how to analyze a repeated measures design using anova in minitab. Author kelly rose view bio. In this article, we described a practical method for selecting a sample size for repeated measures designs and provided an. Using a dental pain study as a driving example, we provide guidance for selecting an appropriate sample size for testing a time by treatment interaction for studies with repeated measures. Web estimation and hypothesis testing. We broke up the analysis into three parts.
PPT Repeated Measures Designs PowerPoint Presentation, free download
B = numbers of levels of iv2) That is, each unit provides at least one data point for each level of one or more independent variables. Penn state's department of statistics. It is a randomized block design in which each experimental unit serves as a blocking variable. To learn more about anova tests, read my anova overview.
For Example, In A Design With 2 Ivs, The Anova Is Described As A X B Anova.
(a = number of levels of iv1; Georgia state university, atlanta, georgia. Web a repeated measures design is a type of randomized block design. Using a dental pain study as a driving example, we provide guidance for selecting an appropriate sample size for testing a time by treatment interaction for studies with repeated measures.
That Is, Each Unit Provides At Least One Data Point For Each Level Of One Or More Independent Variables.
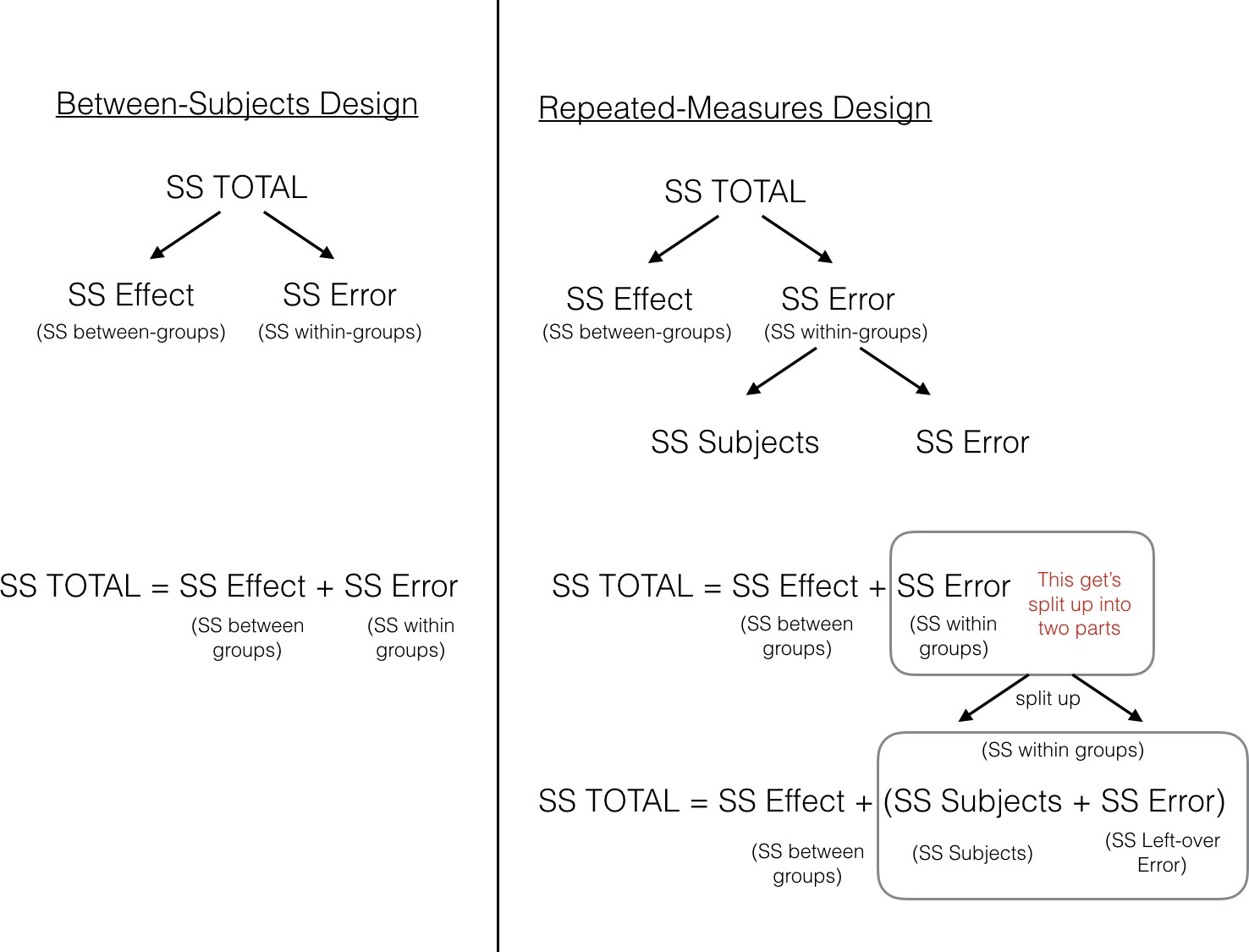
Web repeated measures design is an experimental design where the same participants participate in each independent variable condition. Web the defining characteristic of repeated measures designs is the fact that independent units— usually participants—are “crossed with” at least one of the independent variables; It is a randomized block design in which each experimental unit serves as a blocking variable. Repeated measures analysis of variance (ranova) is one of the most commonly used statistical approaches to repeated measures designs.
Learn About Repeated Measures Design.
The first class uses summary statistics to condense the repeatedly measured information to a single number per subject. Web however, the plethora of inputs needed for repeated measures designs can make sample size selection, a critical step in designing a successful study, difficult. Instructor betsy chesnutt view bio. Using a dental pain study as a driving example, we provide guidance for selecting an appropriate sample size for testing a time by treatment interaction for studies with repeated measures.
In Practice, The Critical Task Of Selecting A Sample Size For Studies With Repeated Measures Can Be Daunting.
Author kelly rose view bio. Evaluate the significance of repeated measures design given its advantages and. Web in this post, i’ll explain how repeated measures designs work along with their benefits and drawbacks. For instance, repeated measures are collected in a longitudinal study in which change over time is assessed.
The first class uses summary statistics to condense the repeatedly measured information to a single number per subject. We broke up the analysis into three parts. B = numbers of levels of iv2) For instance, repeated measures are collected in a longitudinal study in which change over time is assessed. Web the defining characteristic of repeated measures designs is the fact that independent units— usually participants—are “crossed with” at least one of the independent variables;